Applications Details
Check out our applications
Applications
Education
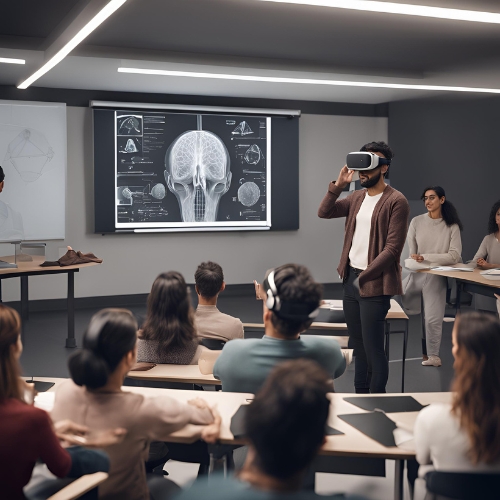

Our Radio Anatomical Interactive Library, enriched with AR/VR and 3D-printed models, offers several benefits for both students and medical professionals. By bridging the gap between theoretical learning and practical application, these advanced tools elevate the quality of medical education and clinical practice, fostering confidence, competence, and innovation.
- Learning: For students in medicine, nursing, and other health-related fields, these tools provide an immersive, hands-on approach to learning that enhances spatial understanding and retention of complex anatomical structures as well as specific pathological conditions and case studies. AR/VR technologies allow learners to explore dynamic simulations, practice procedures in a risk-free virtual environment, and visualize conditions in ways that traditional methods cannot replicate. This can revolutionize the way teaching is delivered, providing the students with the possibility of being part of the active learning experience.
- Benefits for Medical Professionals: Extended Reality (XR) in a shared environment allows two or more individuals to collaborate on the same virtual project, regardless of their physical locations, creating a seamless and interactive workspace. This eliminates geographical barriers, reduces the need for costly travel, and accelerates decision-making processes. Moreover, shared XR environments enhance learning and training, enabling teams to simulate complex scenarios collaboratively, practice problem-solving, and refine their approaches together.
For a comprehensive understanding of the integration of 3D printing technology into surgical planning and medical education, delve into our Handbook of Surgical Llanning and 3D Printing. Designed for educators and professionals, it offers practical guidance on creating accurate anatomical models, fostering enhanced learning experiences, and improving clinical outcomes.
Applications
Training and Surgical Planning
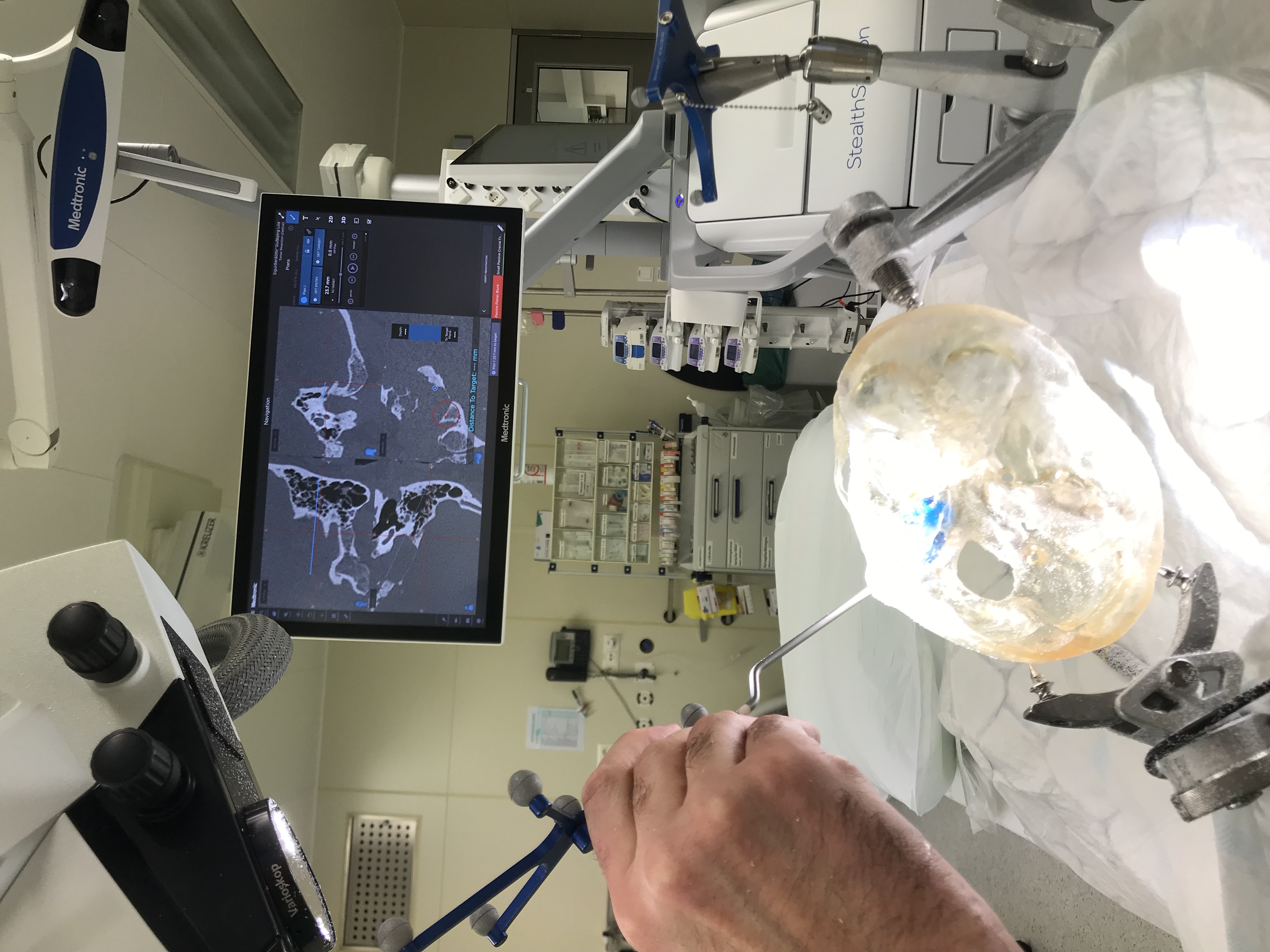
AR/VR and 3D printing, groundbreaking and well-established technologies, are revolutionizing healthcare, particularly in surgical planning. This innovative approach leverages advanced imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans to create precise, life-like anatomical models. These models enable surgeons to better understand complex cases, refine surgical strategies, and enhance outcomes—ushering in a new era of personalized medicine.
- Workflow: The process begins with the acquisition of high-resolution medical images, such as those from Computed Tomography (CT) or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Using specialized software, experts isolate a specific region of interest, converting it into a detailed 3D digital model, producing an accurate replica of the patient’s anatomy. From here, the model is then optimized for AR/VR implementation or brought to life through state-of-the-art 3D printing. Surgeons use these interactive models to simulate procedures, improve precision, and optimize patient care.
- Beyond Practical Relevance: 3D printing and AR/VR for surgical planning are more than technological innovations: they are a tool for transformative care. By enabling precise pre-surgical preparation, they significantly improve clinical outcomes, reduce operative time, and lower healthcare costs. Moreover, these models provide a hands-on learning experience for medical professionals and help the patients to understand the procedure they will undergo.
- Long-Lasting Expertise: Since 2005, the Institute of Biomedical and Neural Engineering (IBNE) has been at the forefront of integrating 3D printing into surgical planning, likely establishing the world’s first dedicated service in this field. This groundbreaking initiative, developed in collaboration with Landspítali University Hospital and Reykjavik University, continues to set the standard for innovation. Today, surgeons and healthcare providers rely on these models to tackle the most challenging clinical cases with confidence and precision.

